Armamentarium. It’s a big word. It’s what we in the U.S. like to call a fifty-cent word. An armamentarium refers to the full range of resources that are available to tackle a problem, often in the arena of health care.
Today, we have an unequivocal need to expand the contraceptive armamentarium for women around the world.
In some cases, this means expanding access to existing, underutilized family planning methods. In too many settings, women do not have adequate access to a full range of options, including long-acting and permanent contraceptive methods. Barriers to access include frequent stock-outs of commodities; a lack of adequate health care facilities or trained staff to administer contraceptives, especially in rural areas; prohibitively expensive client fees; a lack of comprehensive, accurate information for clients; a provider bias against the provision of long-acting methods to some women; and opposition from family members or community institutions.
This week, over 3,000 program implementers, health care providers, researchers, faith-based leaders, donors and policymakers gather in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia for the third International Conference on Family Planning. The theme of the week-long event is “Full Access, Full Choice.” The organizers explain that this is more than just a conference; it is part of a movement to garner commitments globally to implement evidence-based solutions targeting the persistent barriers to access that women and men face every day.
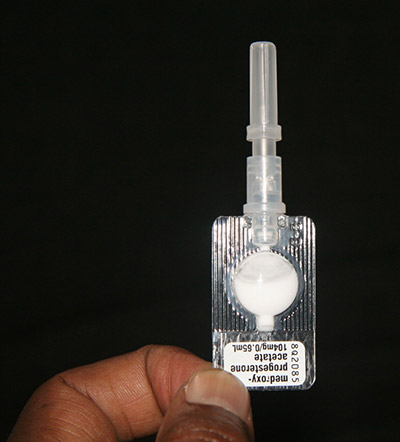
In addition to identifying effective service delivery and policy approaches to increase access to existing methods, we must also take advantage of this moment in Addis to make a long-term commitment to expand the contraceptive armamentarium to include new, innovative methods. The basket of family planning methods available has remained largely unchanged for several decades. There are gaps in the method mix that, if filled, could result not only in increased uptake of contraceptives by women, but also in improved continuation rates by better meeting individuals’ needs and desires.
Continue reading

 Self-management. Self-testing. Self-awareness. These are three pillars of self-care interventions that can help promote the sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) of women, men and youth according to
Self-management. Self-testing. Self-awareness. These are three pillars of self-care interventions that can help promote the sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) of women, men and youth according to 